typescript
tsc
bash
npm install -g typescript
tsc --init --target es2020 --module es2020 --lib es2020基础
类型标注
const/var/let/function/class
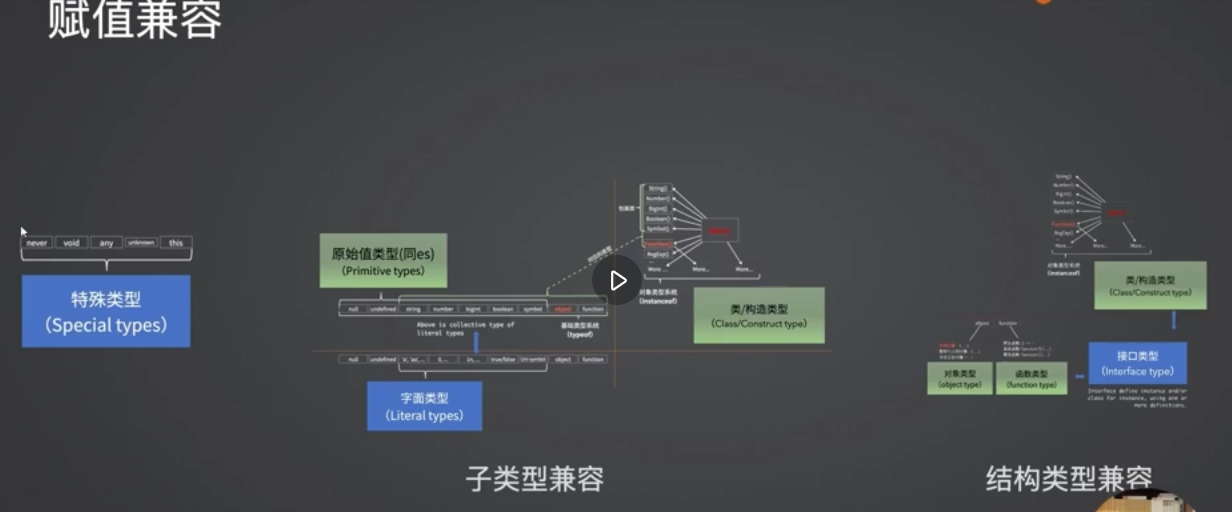
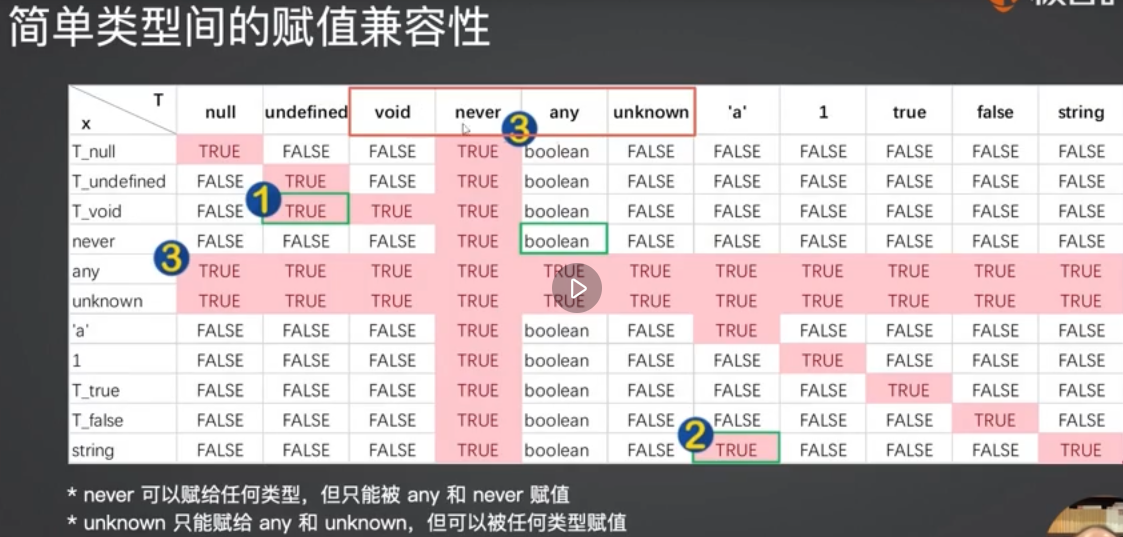
类型兼容
子类型可以赋值给父类型
| 字面类型 | 原始类型 | 包装类型 | Object(祖先类) | Empty{}(空接口/空白对象) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'abc' | string | String | Object | Empty |
| {...} | object | Obejct | Empty |
- 特殊类型 this/nerver/void/any/unknown
- 字面类型:原始值类型、类/构造兼容(子类型兼容)(赋值兼容)
- 接口类型:对象类型、函数类型、类/构造兼容(结构类型兼容)(赋值兼容)
交叉、联合类型
- 基础类型的交叉联合
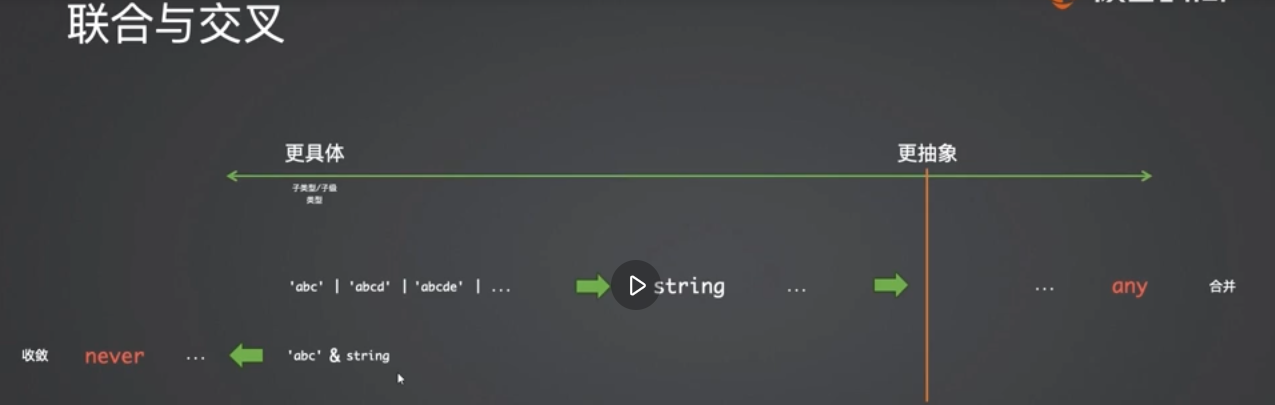
- 联合:往合并方向 -> any (并集)
- 交叉:收敛方向 -> never (交集)
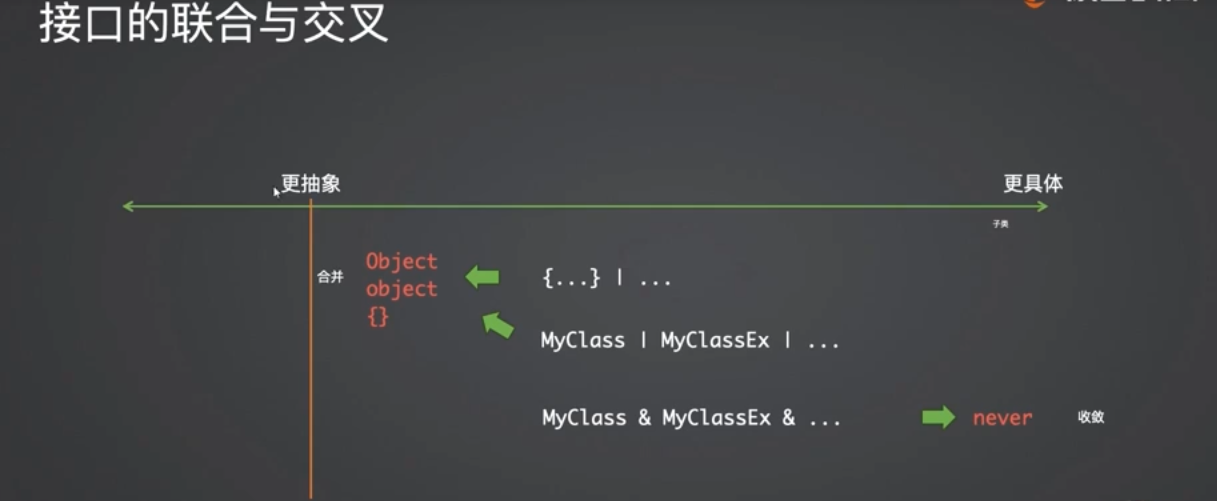
- 接口类型的交叉联合
 ts
ts/* 接口的联合 - 1、接口联合类型可以被求值(结果是“Bird与Horse的公共父类”) - 2、求值并不一定有意义 - 3、 type Animal = Omit<T, never> 获得是属性的交集 */ interface Animal { weight: string | number; leg: number; } interface Bird extends Animal { weight: number; wings: number; } interface Horse extends Animal { weight: string; id: string; } type T = Bird | Horse; // type Animal = Omit<T, never>; // clone let bird!: Bird; let horse!: Horse; let x1: T = bird; let x2: Animal = bird; let x3: Bird | Horse = bird;ts/* 接口的交叉 - 1、会深度遍历每一个成员的交叉(例如weight的类型交叉结果是never) - 2、交叉类型总是尽量向never收敛的 - 3、 type BirdAndHorse = Omit<T, never> 获得是属性的并集 */ interface Bird { weight: number; leg: number; wings: number; } interface Horse { weight: string; leg: number; id: string; } type T = Bird & Horse; // & undefined & void & null & ... type BirdAndHorse = Omit<T, never>; // clone // class MyClass implements T { // class MyClass implements Bird, Horse { class MyClass implements BirdAndHorse { weight: never; leg: number; id: string; wings: number; } let x:MyClass = new MyClass;
接口&类型别名
- 接口与类型别名区别
- 相同:
- 描述对象的形状和函数签名,被拓展
- 不同:
- 类型别名:用于一些其他类型,比如原始类型、联合类型和元组
- 接口可以定义多次,会被自动合并为单个接口
- 相同:
ts
// type(功能更多)
type Name = string;
// tuple
type Data = [number, string];
// object
type PartialPointX = { x: number };
type PartialPointY = { y: number };
// union
type PartialPoint = PartialPointX | PartialPointY; // 联合类型
const obj:PartialPoint = {
x:1
}
const obj2:PartialPoint = {
y:1
}
const obj3 : PartialPoint = {
x:1,
y:2,
}
// 接口(自动合并)
interface Point {
x: number;
}
interface Point {
y: number;
}
const point: Point = { x: 1, y: 2 };类
ts
// @ts-nocheck Disables semantic checking in a JavaScript file.
class MyClass {
// private instance fields, TS3.8, `Class Fields` feature family in ES2022
#a = 10;
#f() { };
get #f2() { return 'a'}
// private class fields
// - Static and instance elements cannot share the same private name
static #a2 = 10;
static #foo2() { };
// public instance fields
b1 = 100;
b2 = 'a';
b3 = ()=>{ };
// public class fields
static d1 = 100;
static d2 = 'a';
static d3 = ()=>{ };
constructor() { }
c1() { }
// get/set, async and/or *
get c2() {
return 1;
}
// static members, and more
// ...
// class static block, TS4.4, ES2022
static { }
// auto-accessor, TS4.9, ES proposal stage 1
accessor x = 100;
}类实现接口 implements
ts
interface Point {
x: number;
y: number;
}
class SomePoint implements Point {
x = 1;
y = 2;
}
type Point2 = {
x: number;
y: number;
};
class SomePoint2 implements Point2 {
x = 1;
y = 2;
}
// A class can only implement an object type or intersection of object types with statically known members.
type PartialPoint1 = { x: number } | { y: number };
class SomePartialPoint implements PartialPoint1 { // 与类型别名有不同
// Error
x = 1;
y = 2;
}
// ok
type PartialPoint2 = { x: number } & { y: number };
class SomePartialPoint implements PartialPoint2 {
x = 1;
y = 2;
}- implements 实现:class专有
- extends 继承:class、interface都可以
联合类型
ts
// 1
let num: 1 | 2 = 1;
type EventNames = "click" | "scroll" | "mousemove";
// 2 可辨识联合
type PartialPointX = { x: number };
type PartialPointY = { y: number };
type PartialPoint = PartialPointX | PartialPointY;
let point: Point = {
x: 1,
y: 1,
};
let point1: Point = {
x: 1,
};
let point2: Point = {
y: 1,
};交叉类型
ts
// 接口
interface X {
c: string;
d: string;
}
interface Y {
e: string;
}
type XY = X & Y;
let value: XY = {
c: "1",
d: "1",
e: "1",
};
// 类型
type PartialPointX = { x: number };
type Point = PartialPointX & { y: number };
let point: Point = {
x: 1,
y: 1,
};元祖
- 1、限制长度
- 2、对每一个成员限定类型
- 3、主要用于函数参数类型
同名策略
- 重载 overload
- 覆盖 class override
- 合并
- 两个同名接口合并
- 同名类、接口合并
枚举
- 枚举类型是联合类型、不是object,在JavaScript中是一个对象
ts
enum X {
a,
b = Number(2),
c = "c"
}
const enum Y {
a,
c = "c"
}
type T1 = keyof typeof X
// ^?
// type T1 = "c" | "a" | "b"
type T2 = keyof typeof Y
// ^?
// type T1 = "c" | "a"
type V1 = `${X}`
// ^?
// type V1 = string 读取不出来
type V2 = `${Y}`
// ^? type
// V2 = "c" | "0" 可以读取到ts
const Up = 111
enum T {
Up // 0
}
console.log(T)泛型
ts
interface activity {
activityName: string;
activityId: string;
}
//数组泛型表示数组
const nodeList: Array<activity> = [];
const nodeList: Ref<Array<activity>> = ref([]);高级类型操作符
- Awaited 获得Promise返回的类型
ts
type A = Awaited<Promise<string>>;
// type A = string
type B = Awaited<Promise<Promise<number>>>;
// type B = number
type C = Awaited<boolean | Promise<number>>;
// type C = number | boolean- Partial属性设置为可选
ts
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
address: string;
}
type PartialPerson = Partial<Person>;
const partialPerson: PartialPerson = {
name: "Alice"
};
console.log(partialPerson);
// 输出:{ name: "Alice" }- ReturnType 获取函数类型的返回值类型
ts
function add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
type AddReturnType = ReturnType<typeof add>; // number
const result: AddReturnType = add(3, 5);
console.log(result); // 输出:8- Record 给每一个属性赋值
ts
type CatName = "miffy" | "boris" | "mordred";
interface CatInfo {
age: number;
breed: string;
}
const cats: Record<CatName, CatInfo> = {
miffy: { age: 10, breed: "Persian" },
boris: { age: 5, breed: "Maine Coon" },
mordred: { age: 16, breed: "British Shorthair" },
};- Pick 选出你要的属性
ts
interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
completed: boolean;
}
type TodoPreview = Pick<Todo, "title" | "completed">;
const todo: TodoPreview = {
title: "Clean room",
completed: false,
};- Omit 排除你要的属性
ts
interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
completed: boolean;
createdAt: number;
}
type TodoPreview = Omit<Todo, "description">;
const todo: TodoPreview = {
title: "Clean room",
completed: false,
createdAt: 1615544252770,
};- Exclude 排除联合类型/排除key
ts
type T0 = Exclude<"a" | "b" | "c", "a">;
// type T0 = "b" | "c"
type T1 = Exclude<"a" | "b" | "c", "a" | "b">;
// type T1 = "c"
type T2 = Exclude<string | number | (() => void), Function>;
// type T2 = string | number
type Shape =
| { kind: "circle"; radius: number }
| { kind: "square"; x: number }
| { kind: "triangle"; x: number; y: number };
type T3 = Exclude<Shape, { kind: "circle" }>
// type T3 = {
// kind: "square";
// x: number;
// } | {
// kind: "triangle";
// x: number;
// y: number;
// }类型断言
- as const
ts
declare function handleRequest(url: string, method: "GET" | "POST"): void;
const req = { url: "https://example.com", method: "GET" };
handleRequest(req.url, req.method);
// Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type '"GET" | "POST"'.
// req.method 被推断为字符串,而不是“GET”ts
// Change 1:
const req = { url: "https://example.com", method: "GET" as "GET" };
// Change 2
handleRequest(req.url, req.method as "GET");
// Change 3
// 您可以使用 as const 将整个对象转换为类型文字
const req = { url: "https://example.com", method: "GET" } as const;
// const req: {
// readonly url: "https://example.com";
// readonly method: "GET";
// }
handleRequest(req.url, req.method);- satisfies 自动推导出来的类型
ts
type Route = { path: string; children?: Routes }
type Routes = Record<string, Route>
const routes:Routes = {
AUTH: {
path: "/auth",
},
}
routes.AUTH.path // ✅
routes.AUTH.children // ✅
routes.NONSENSE.path // ✅ts
// satisfies
type Route = { path: string; children?: Routes }
type Routes = Record<string, Route>
const routes = {
AUTH: {
path: "/auth",
},
} satisfies Routes
routes.AUTH.path // ✅
routes.AUTH.children // ❌ routes.auth has no property `children`
routes.NONSENSE.path // ❌ routes.NONSENSE doesn't exist- as const & satisfies
ts
// 只用 satisfies
function navigate(path: '/' | '/auth') { ... }
const routes = {
HOME: { path: '/' }
} satisfies Routes
navigate(routes.HOME.path)
// ❌ Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type '"/" | "/auth"'
// as const & satisfiests
const routes = {
HOME: { path: '/' }
} as const satisfies Routes
navigate(routes.HOME.path) // ✅ - as desired
navigate('/invalid-path') // ❌ - as desired- 参考:https://article.juejin.cn/post/7240805459288113208
- 参考:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2212264
实践
兼容旧代码
- 场景:
- 项目迁移,新项目使用ts,为了兼容旧项目的代码,
- 兼容windows:全局变量、全局方法
- 解决思路:
- 一个框架,在IIEF模式中使用,方法全部为暴露在window上的,继承其类型
interface Window extends p5 - 自定义方法,则添加到 interface Window 中
- 一个框架,在IIEF模式中使用,方法全部为暴露在window上的,继承其类型
ts
import type p5 from "p5"
declare var read: () => void;
declare var write: (code:string) => void;
declare global {
interface Window extends p5 {
read: () => void;
write:(code:string) => void;
}
}
export {};泛型使用
- 泛型是什么
- 泛型其实就是封装相同操作的包裹体
- 重复实现的过程,进行抽离,每次传入不同的类型值
- 场景:
- 在react中父组件定义一个响应式的对象
- 多个子组件对其中部分属性进行更新(非常常见的操作)
- 解决:
- 更新的操作都是一样的,定义泛型
- 更新的对象的属性不一样,进行传入
- 多个地方都可以使用定义的泛型
ts
// 定义 type 泛型
export type UpdateStateType<T> = (newState: Partial<T>)=> void;
export interface StatePropsType <T>{
updateState: T
}
// 类型值
export type OrderStateType = {
aaa: string ;
bbb: number ;
ccc: string
}
// 传入
export type UpdateOrderStateType = UpdateStateType<OrderStateType>
export type OrderStatePropsType = StatePropsType<UpdateOrderStateType>ts
// 在react中使用
// 父组件 page.tsx
import Home from "./Home";
import {OrderStateType,UpdateOrderStateType} from "@/type/State"
export default function Home() {
const [state,setState] = useState<OrderStateType>({
aaa:"",
bbb:0,
ccc:""
})
const updateState:UpdateOrderStateType = (newState) => {
setState(prevState => ({ ...prevState, ...newState }));
};
return (
<Home updateState={updateState}>
<div>{state.aaa}</div>
</Home>
);
}
// 子组件 Home.tsx
import {OrderStatePropsType} from "./State"
const Home: React.FC<OrderStatePropsType> = ({updateState}) => {
const handle = () => {
updateState({aaa:"111"})
}
return <div></div>
}
export default Home函数声明 vs 箭头函数
- 场景
- react中一个组件可以是函数声明导出,也可以是箭头函数导出
- 有什么区别吗
- 区别 (写法区别)
ts
// React.FC<OrderStatePropsType> 是Home这个方法的类型
const Home: React.FC<OrderStatePropsType> = ({updateState}) => {
const handle = () => {
updateState({aaa:"111"})
}
return <div></div>
}
export default Homets
// 函数声明写法
// 使用 ReturnType<React.FC<OrderStatePropsType>> 函数类型的返回值类型
// 参数类型判断 {updateState}:OrderStatePropsType
export default function Home ({updateState}:OrderStatePropsType):ReturnType<React.FC<OrderStatePropsType>>{
const handle = () => {
updateState({aaa:"111"})
}
return <div></div>
}jsDoc
- JSDoc 是在 js 的注释里通过 @type、@typedef、@template、@param 等来定义类型,然后开启 checkJS 和 allowJS 的配置之后,tsc 就可以对 js 做类型检查 参考:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2351090