NodeJs
学习资料
文档
node 命令行
# 执行 esm 脚本
node --input-type=module index.js
node index.mjs全局变量
__dirname:当前Node运行环境所在目录的绝对路径。 __filename:当前运行的脚本的绝对路径 (包含文件名) global:其表示Node所在的全局环境,类似于浏览器中的window对象。 process:其指向Node内置的process模块,允许开发者使用此对象操作当前进程。 console:其指向Node内置的console模块,提供命令行环境中的标准输入、标准输出功能,比如console.log ("electron") ;
Process
process 对象提供有关当前 Node.js 进程的信息并对其进行控制。 process.cwd() 方法返回 Node.js 进程的当前工作目录。 process.env 属性返回一个包含用户环境的对象 process.platform 返回一个字符串,用于标识当前运行 Node.js 的操作系统平台。
- 'aix' IBM AIX 操作系统。常用于大型企业和工业领域,运行在 IBM 的 Power 系列服务器上。
- 'darwin' macOS 操作系统。苹果公司开发的 Unix 系统,用于 Mac 系列设备。
- 'freebsd' FreeBSD 操作系统。一个开源的类 Unix 系统,广泛用于网络服务器和存储系统。
- 'linux' Linux 操作系统。一个开源操作系统,广泛用于服务器、嵌入式设备和个人电脑。
- 'openbsd'OpenBSD 操作系统。一个以安全性为核心的类 Unix 操作系统,适用于防火墙和高安全性场景。
- 'sunos'SunOS 操作系统。Solaris 的前身,曾由 Sun Microsystems 开发,用于企业级硬件系统。
- 'win32 'Windows 操作系统。微软开发的操作系统,包括 32 位和 64 位版本,但始终标记为 'win32'。
module
一旦一个模块被导入到运行环境中,就会被缓存。 当再次尝试导入这个模块时,就会读取缓存中的内容,而不会重新加载一遍这个模块的代码。
url
fileURLToPath
此函数确保百分比编码字符的正确解码以及跨平台有效的绝对路径字符串。 主要用于转为path,在需要加载path的地方做转换,例如 webPreferences{preload:'path'}
// esm 写法
import { fileURLToPath } from 'node:url';
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url);
new URL('file:///C:/path/').pathname; // Incorrect: /C:/path/
fileURLToPath('file:///C:/path/'); // Correct: C:\path\ (Windows)
new URL('file://nas/foo.txt').pathname; // Incorrect: /foo.txt
fileURLToPath('file://nas/foo.txt'); // Correct: \\nas\foo.txt (Windows)
new URL('file:///你好.txt').pathname; // Incorrect: /%E4%BD%A0%E5%A5%BD.txt
fileURLToPath('file:///你好.txt'); // Correct: /你好.txt (POSIX)
new URL('file:///hello world').pathname; // Incorrect: /hello%20world
fileURLToPath('file:///hello world'); // Correct: /hello world (POSIX)// esm 写法
new URL('./preload.js',import.meta.url).href // file:///D:/WorkSpace/****/preload.js
import.meta.resolve('./preload.js') // file:///D:/WorkSpace/****/preload.js
fileURLToPath(new URL('./preload.js',import.meta.url).href) // D:\WorkSpace\****\preload.js
fileURLToPath(import.meta.resolve('./preload.js')) // D:\WorkSpace\****\preload.jsformat
// commonjs 写法
let URL = require('url')
// 第一个参数 WHATWG URL
// WHATWG URL (Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group URL) 指的是 WHATWG 组织制定的 URL 标准,它定义了 URL 的解析、构造、规范化等操作。 这个标准的目标是使不同的浏览器和 JavaScript 环境对 URL 的处理方式保持一致,并提供一套清晰的 API 供开发者使用。
URL.format({
pathname: path.join(__dirname, 'index.html'),
protocol: 'file',
})
// file://d:\**\**\index.html// esm 写法
// 第一个参数是一个 url
import url from 'node:url';
const myURL = new URL('https://a:b@測試?abc#foo');
console.log(myURL.href);
// Prints https://a:b@xn--g6w251d/?abc#foo
console.log(myURL.toString());
// Prints https://a:b@xn--g6w251d/?abc#foo
console.log(url.format(myURL, { fragment: false, unicode: true, auth: false }));
// Prints 'https://測試/?abc'参考:https://nodejs.org/docs/latest/api/url.html
fs
existsSync / exists
文件以及路径是否存在,一般在读取、删除、创建时做判断处理
import { existsSync } from 'node:fs';
if (existsSync('/etc/passwd'))
console.log('The path exists.');readFileAsync / readFile / promises.readFile
const fs = require('fs');
// 同步
try {
const data = fs.readFileSync('example.txt', 'utf8');
console.log('File content:', data);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error reading file:', err);
}
// 异步
fs.readFile('example.txt', 'utf8', (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.error('Error:', err);
}
});
// 异步
try {
const data = await fs.promises.readFile('example.txt', 'utf8');
console.log('File content:', data);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error:', err);
}wirteFileAsync / wirteFile / promises.wirteFile
同上 readFile
export function writeFileAsync(content: string | Buffer, outputFilePath: string): Promise<void> {
return fs.promises.writeFile(outputFilePath, content)
}import { writeFile } from 'node:fs/promises';
import { Buffer } from 'node:buffer';
try {
const controller = new AbortController();
const { signal } = controller;
const data = new Uint8Array(Buffer.from('Hello Node.js'));
const promise = writeFile('message.txt', data, { signal });
// Abort the request before the promise settles.
controller.abort();
await promise;
} catch (err) {
// When a request is aborted - err is an AbortError
console.error(err);
}realpath / realpathSync / promises.realpath / realpath.native
- 通过解析 .、.. 和符号链接异步地计算规范路径名。
- fs.realpath.native
- 使用的是操作系统的原生 API(如 Windows 上的 Win32 API 或 Unix 系统调用)来解析路径。
- 性能更高,特别是在处理符号链接(symlinks)时。
const tempPath = app.getPath('temp');
// tempPath => C:\Users\ABCDE~1.FGH\AppData\Local\Temp
const resolvedPath = fs.realpathSync(tempPath);
console.log(resolvedPath); // 将输出长文件名路径lstatSync / lstat
获取目标路径的详细文件信息 (文件状态)。 lstatSync() 不会跟随符号链接,而是返回符号链接本身的状态。
const fs = require('fs');
const dirPath = './example'; // 替换为实际路径
try {
const stats = fs.lstatSync(dirPath);
if (stats.isFile()) {
console.log(`${dirPath} 是一个文件`);
} else if (stats.isDirectory()) {
console.log(`${dirPath} 是一个目录`);
} else if (stats.isSymbolicLink()) {
console.log(`${dirPath} 是一个符号链接`);
} else {
console.log(`${dirPath} 是其他类型`);
}
console.log('文件大小 (字节):', stats.size);
console.log('创建时间:', stats.birthtime);
console.log('修改时间:', stats.mtime);
} catch (err) {
console.error('无法读取路径:', err.message);
}statSync
如果路径是符号链接,fs.statSync() 会返回符号链接指向目标的状态
const linkPath = './symlink'; // 假设是符号链接
const stats = fs.statSync(linkPath); // 获取目标的信息
console.log(stats.isSymbolicLink()); // false, 这里指向的目标不是符号链接
const lstats = fs.lstatSync(linkPath); // 获取符号链接本身的信息
console.log(lstats.isSymbolicLink()); // true, 符号链接本身mkdir
创建文件夹
import { mkdir } from 'node:fs/promises';
try {
const projectFolder = new URL('./test/project/', import.meta.url);
const createDir = await mkdir(projectFolder, { recursive: true });
console.log(`created ${createDir}`);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.message);
}rmdir rm unlink
- rmdir 删除目录
- rm 删除文件、空目录或非空目录
- unlink 删除
- 如果路径引用符号链接,则删除该链接不会影响该链接引用的文件或目录。
- 如果该路径引用的文件路径不是符号链接,则该文件将被删除。
- 如果路径指向一个目录,unlink 将会失败并抛出一个错误。
const stats = fs.lstatSync(dirPath)
if (stats.isDirectory()) {
return fs.promises.rm(dirPath, { recursive: true })
}
//
return fs.promises.unlink(dirPath)link / symlink
- link 创建硬链接
- symlink 创建软链接
// const fs = require('fs').promises;
import fs from 'fs/promises'
import path from 'path'
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url'
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url)
const __dirname = path.dirname(__filename)
async function createHardLinkFile() {
// 关键点:硬链接本质是一个名字,其实不受路径的影响
// await fs.link('./test/test.txt', './test2/hardlink.txt'); // 创建硬链接
const targetPath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'test', 'test.txt')
const hardlinkPath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'test1', 'hardlink.txt')
await fs.mkdir(path.dirname(hardlinkPath), { recursive: true })
await fs.link(targetPath, hardlinkPath)
console.log('创建完成')
}
createHardLinkFile().catch(console.error)
async function createSoftLinkDir() {
const targetPath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'test')
const symlinkPath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'test3softlink')
let relativeTarget = path.relative(path.dirname(symlinkPath), targetPath)
console.log('soft link target relative path:', relativeTarget)
await fs.symlink(relativeTarget, symlinkPath, 'dir')
console.log('创建完成')
}
createSoftLinkDir().catch(console.error)
async function createSoftLinkFile() {
const targetPath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'test', 'test.txt')
const symlinkPath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'test2', 'softlink.txt')
// 关键点:targetPath 是相当于 symlinkPath的
let relativeTarget = path.relative(path.dirname(symlinkPath), targetPath)
relativeTarget = relativeTarget.split(path.sep).join('/')
console.log('soft link target relative path:', relativeTarget)
await fs.mkdir(path.dirname(symlinkPath), { recursive: true })
await fs.symlink(relativeTarget, symlinkPath, 'file')
// await fs.symlink('./test/test.txt', './test2/test.txt', 'file') // 创建的软连接打开异常
console.log('创建完成')
}
createSoftLinkFile().catch(console.error)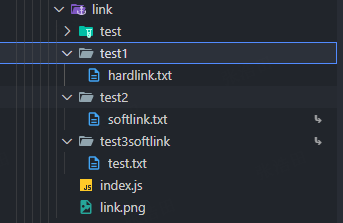
util
util.promisify
一个基于回调的函数转换为一个返回 Promise 的函数
const util = require('util');
function asyncMethod(x, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const result = x * 2;
callback(null, result); // 第一个参数通常是 error
}, 500);
}
const promiseMethod = util.promisify(asyncMethod);
promiseMethod(5)
.then(result => {
console.log(result); // 输出: 10 (大约 500ms 后)
})
.catch(err => {
console.error(err);
});path
path.isAbsolute()
确定 path 是否为绝对路径
// 在 POSIX 上:
path.isAbsolute('/foo/bar'); // true
path.isAbsolute('/baz/..'); // true
path.isAbsolute('qux/'); // false
path.isAbsolute('.'); // false
// 在 Windows 上:
path.isAbsolute('//server'); // true
path.isAbsolute('\\\\server'); // true
path.isAbsolute('C:/foo/..'); // true
path.isAbsolute('C:\\foo\\..'); // true
path.isAbsolute('bar\\baz'); // false
path.isAbsolute('bar/baz'); // false
path.isAbsolute('.'); // falsecommomjs获取文件路径 path.resolve(__dirname, './**/*/')
const path = require('path');
// 获取当前文件所在的目录
const currentDir = __dirname;
// 获取当前文件的完整路径
const currentFile = __filename;
// 构建相对路径
const relativePath = path.resolve(__dirname, './fs/1/2');
console.log('Current directory:', currentDir);
console.log('Current file:', currentFile);
console.log('Relative path:', relativePath);zlib
import fs from 'node:fs'
import zlib from 'node:zlib'
/**
* 解压文件
* @param stream 文件流
* @param outputFilePath 文件写入路径
*/
export function unzipFile(
src: NodeJS.ReadableStream | string,
dest: NodeJS.WritableStream | string,
): Promise<void> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
const readStream = typeof src === 'string' ? fs.createReadStream(src) : src
const writeStream = typeof dest === 'string' ? fs.createWriteStream(dest) : dest
// 创建一个解压流,用于处理 .gz 格式文件
const gunzip = zlib.createGunzip()
// 数据从 readStream 读入,经过 gunzip 解压后,写入 writeStream
readStream.pipe(gunzip).pipe(writeStream)
writeStream.on('finish', () => {
resolve()
})
writeStream.on('error', (e) => {
reject(new Error('Failed when write file', { cause: e }))
})
} catch (e) {
reject(new Error('Unzip Failed', { cause: e }))
}
})
}buffer
- 浏览器和 Node.js 都支持 ArrayBuffer 和 Uint8Array,但它们在实现上有所不同。
- ArrayBuffer 的本质: 浏览器的 ArrayBuffer 的确就是一块连续的内存空间,它本身不提供任何读写数据的方法。
- Uint8Array 的作用: Uint8Array 作为视图,提供了操作 ArrayBuffer 这块内存的方式,让你能够以 8 位无符号整数的形式来读取和写入数据。
- Node.js 的 Buffer: Node.js 的 Buffer 最早出现,也是用于操作内存的,它在 Uint8Array 出现之前就已经存在,并提供了一些额外的便利方法。
- Uint8Array 的标准化: Uint8Array 出现之后,成为了 JavaScript 中处理二进制数据的更标准的方式,并且被浏览器和 Node.js 同时支持。
stream 流
- 流
- 流的本质: 流的本质是将数据分成多个小块进行传输和处理。
- 无论是否知道数据的总长度,都可以使用流。
- Content-Length 的作用: Content-Length 只是告诉客户端数据的总长度,方便客户端计算下载进度等。
- 发送本地磁盘上的静态文件。
- 发送从数据库中读取的完整数据。
- Transfer-Encoding: chunked 的作用: Transfer-Encoding: chunked 是一种特殊的流式传输方式,用于服务器无法预先知道数据总长度的情况。
- 动态生成的内容(例如,实时日志、服务器推送)。
- 从多个来源组合数据。
- 需要进行复杂处理才能确定数据总长度的情况。